Who Starts Betting In Texas Holdem
- One of my favourite pieces of training is the Upswing Poker Lab which is run by the famous poker pro-Doug Polk – this course starts at the very basics of poker, and will teach you the fundamentals of Cash games MTTs and live poker turning you into a well-rounded player that can hold your own in any texas holdem game.
- Place the blinds (starting bets) or 'ante up.' In poker, bets are placed at the beginning of the game in one of 2 ways. In Texas Hold’em, the player next to the dealer typically places a small blind bet that’s half of the usual minimum bet, while the player to that person’s left places a big blind that’s at least the minimum bet.
- Texas Holdem Betting Actions. When the winner is decided and takes down the bot, another Texas Holdem hand starts. It follows the same game flow starting with posting blinds and dealing the cards and then moving through all of the betting rounds once again.
Poker is played with various betting structures and rules for how much you can bet, raise or check-raise.
In some formats and games, for example, you can only bet a certain fixed amount for any bet and the amount of bets per round are capped; in other formats you can bet all your money in one go at any time.
Texas Hold’em can be a hard poker game to master; however, learning can be a rewarding challenge. In fact, getting to understand Texas Hold'em terms such as “bluffing”, “having position” and “going all-in” are some of the most appealing things about this form of poker. At the start of every hand, each player is dealt two hole (face down) cards. In Texas Hold’em, the person who starts or goes first is dependent on what stage of the hand being played. Before the flop, the first person to act is the player seated directly to the left of the Big Blind. This seat is often referred to as Under The Gun (UTG).
If you've watched poker on TV you're likely most familiar with this form - aka 'No Limit' - which makes for spectacular 'all ins' and exciting showdowns.
The game usually being played on TV is No-Limit Texas Holdem so while these betting rules apply to many different forms of poker, consider these de facto Texas Holdem betting rules.
But No-Limit isn't the only way to make bets in poker. In fact for decades the most commonly played forms of poker were slow, steady 'Limit' betting rounds that kept variance and wild bankroll swings to a minimum. Pot-Limit formats (more on this below) are also quite common (eg Pot-Limit Omaha).
In this beginners guide to poker betting we'll take a look at the most common betting rules in Texas Hold'em and beyond. We'll start with the most popular one, of course - No Limit. It's easier to explain, even though it's not at all easy to master.
Beginners Guide to Poker Betting
No-Limit Poker
In No-Limit Poker, as soon as it's your turn to bet you're allowed to bet all the chips that you have in front of you into the pot. You don't even have to have the most chips at the the table -- you can go 'all in' with whatever you have in your stack.
As we mentioned it makes for great drama at the table and tense, cards exposed Texas Hold'em showdowns where one player is playing for their cash game or tournament life on the turn of a single card.
Don't get confused by the exaggerated scenarios of film or TV though - you still can't throw your car keys or your bearer bonds into the pot as they do it in the movies. You can't even dig into your wallet for more cash in the middle of a hand.
Today's No-Limit poker games always use a rule called 'table stakes.' It means that you can never bet anything above and beyond the money you had on the table when the hand started.
As the sharp observer will have noticed this means that there's a 'limit' to the betting after all. So 'no-limit' poker isn't actually without limits. But for the sake of simplicity, No Limit is the term used to describe it.
Don't make the mistake of thinking that no-limit poker is more dangerous for your bankroll than fixed-limit poker. It all depends on what stakes you play at. A game of Limit Texas Hold'em with blinds of $100/$200 certainly isn't cheaper than a No-Limit Texas Hold'em game with blinds of $1/$2.
Fixed-Limit Poker
In fixed-limit poker, the size of each bet is fixed in advance. In Hold'em and Omaha, the first two betting rounds use bets and raises the size of the big blind (called the small bet). In the following two betting rounds, bets and raises are twice the big blind (called the big bet).

When you specify the size of a fixed-limit game, the convention is to give the size of the small bet and the big bet. If the blinds are $1/$2, you'd say that the game is $2/$4. For the internet generation this may seem a bit odd, and it's different from no-limit and pot-limit poker. Still, it's common use.
Often, the number of raises in each betting round is limited to three or four, after which the betting is 'capped.' This means that you won't be able to put in more than $6 or $8 during the first round of betting in a Texas Hold'em game with blinds at $1/$2.
This rule is often put out of play when only two players remain in the hand, in which case they can continue raising until all their money is in the pot. If they want to, that is.
Don't make the mistake of thinking that fixed-limit poker is easier than no-limit poker. Sure, you don't stand to lose your entire stack after a single mistake, but on the other hand you won't double your stack in one single move either. Fixed-limit is another game altogether and you have to play it differently.
Pot-Limit Poker
In Pot-Limit poker the amount you can bet when it's your turn is limited by the size of the pot. The pot-limit rule goes like this:
- You can raise up to the amount that is in the pot after you have called the previous bet.
This may sound a bit complicated and in practice it can get even trickier. Have courage though; there are some tricks you can use to master the pot bet. Read are in-depth guide to the pot bet here:
Don't make the mistake of thinking that pot-limit poker is safer for your bankroll than no-limit poker. Even if they are limited to the size of the pot, bets in pot-limit poker are generally not smaller than in no-limit.
Most bets in no-limit poker are actually the size of the pot or smaller.
How Betting Rounds Work in Poker
Each poker hand is made up of a number of betting rounds. The number of betting rounds depends on the poker variation.
In Texas Holdem there are four betting rounds. In Seven Card Stud there are five and in Five Card Draw there are just two betting rounds.
Fold, Call or Raise
In each betting round, the betting moves clockwise around the table. Each player in turn must either match the bet of the previous player (call) or get out of the hand (fold).
Or, instead of just calling, when it's your turn to bet you can also choose to bet more than the previous bet (raise).
When all players have either folded or called the last raise, the betting round is over. All bets that have been made during the betting round are added to the pot.
All players who remain in the hand have now put in the same amount. They have all matched the biggest bet in that betting round. You can think of this as a negotiation - players agreeing on the price to see another card.

When the betting round is over, if all players except one have folded, the remaining player wins the pot. If everybody else but you folds, you don't even have to show your cards to win. That's what makes bluffing possible in poker.

The Check
Before a bet has been made in the current betting round, the player whose turn it is can choose not to bet (check). Checking simply means passing on the turn to the next player without making a bet.
If it helps, you can think of checking as calling a zero bet. It it doesn't help you, please just forget about it.
The Check-Raise
Let's say that a player checks and another player puts in a bet. When the betting comes around to the player who checked may either fold, call the additional but - or raise!
If he raises here his move is called a 'check-raise.' This is not really a rule per se but it's still good to know what check-raising means.
Texas Hold'em Betting Order & The Blinds
At the start of each poker hand some players have to make a bet even before the cards are dealt.
This is to create a small pot to compete for. Without those 'forced bets' all players could fold every hand without any cost and poker would probably be a very slow game.
In some poker variations, the forced bets are called Blinds. The player to the left of the dealer puts in the small blind and the next player to the left puts in the big blind.
This is how it works in Texas Hold'em and Omaha. Blinds are 'live bets,' which means that they count as valid bets in the first betting round.
Once the cards have been dealt it is the player to the left of the big blind who starts the first betting round (this position is called 'under the gun'.)
He or she must either match the big blind, fold, or raise. Checking is not an option since the big blind is considered as a valid bet. Remember that you can only check if no player has bet before you in that betting round.
Important note: In subsequent Texas Hold'em betting rounds the player closest to the left of the dealer begins the betting round. SO that means while the small and big blind get to act last in the first round, if they are still in the hand they will act first after the flop is dealt.
The player with (or closest to) the dealer button will act last for the rest of the betting rounds. This is called 'having position' in Texas Hold'em and it is a very important concept for playing proper Texas Hold'em strategy.
Big Blind Has an Option
Normally in a betting round, when all players have either folded or called the current bet, the betting round is over. However, when you play with blinds there is an exception to this rule in the first betting round.
In the first betting round of Texas Holdem or Omaha, if all players fold or call the big blind the player in the big blind has an option: He or she may either check or bet.
Antes Instead of Blinds
Some poker variations use antes instead of blinds. An ante is a forced bet that all players have to put in the pot before the cards are dealt. As opposed to blinds, antes are not live bets. They are just put in the middle to stimulate the betting but do not count in betting for any one player.
When there are no blinds there must be some other rule to decide who begins the betting. In Seven Card Stud the player with the lowest card showing must start by putting in a half or a whole small bet (called bring in).
From there, the betting goes on a usual. Since there's no big blind there's also no big blind option in the first betting round.
The Showdown
When the last betting round is over, if two or more players remain in the hand there is a showdown. Players show down their cards and the best hand wins the pot. If two hands are equally good, the pot is split equally between them.
Who Shows Cards First in Poker Showdown?
- If the pot was raised, it's the player who put in the last raise
- If there was a bet but the pot wasn't raised, it's the player who put in the first bet
- If there was no betting, it's the first remaining player to the left of the dealer
The player who shows first has to show down his or her cards. Then the other remaining players show their cards in clockwise order. If their hands are losing hands, they don't have to show their cards - they can just slide their hands to the dealer without revealing what they hold.
You can, however, always show your cards if you feel like it.
Read More:
More Poker Games Rules
Poker Tools:
In the “old” days of Texas hold’em, players would only bet after the flop if they had something. If they missed the flop and didn’t connect, they would check and wait to see if they improved on the turn. As the game saw new and innovative thinkers working in, this all changed. These bright minds saw that this sort of repetitious behavior was exploitable, and hence continuation betting was born.
In this guide, I’m going to start by walking you through what a continuation bet is. I’ll talk about how effective they were in their early days and how they’ve had to adapt as people caught on to what was going on. Through this process, I’m going to give you an extensive lesson in how these bets can be worked into your game. I’ll talk about the common mistakes people make and how you can correct them.
Basically, I’m going to talk about A LOT. By the end of this guide, you’re going to be able to self-proclaim yourself a continuation-betting wizard.
What Is a Continuation Bet?
Before I can get into the strategic implications of continuation bets and how to implement them, I need to define what is and what is not a continuation bet. A continuation bet is a bet that you make after the flop when you are the pre-flop aggression. Basically, if you raise pre-flop and then elect to bet again after the flop comes out, you are making a continuation bet.
This does not refer to every bet that is made after the flop. It’s only the bets that are “continued” by the pre-flop aggressor. If someone else raises pre-flop and you call and then elect to lead out on the flop, you are not making a continuation bet.
Continuation bets can be made when you have a hand and when you are bluffing. In fact, the term really only came into existence when people started continuing their pre-flop aggression as a bluff.
Why They Are Profitable
To help you better understand the importance and effectiveness of continuation betting, I need to talk about why these bets are profitable. First, they’re profitable when you actually have a hand. When you have the best hand, they allow you to start building a pot. In the old days, though, people knew you had a hand because you would only bet if you did. This means that if you were betting, they would fold unless they had something as well.

But when you start mixing in continuation betting as a bluff, it makes it harder for people to know when you have a hand and when you don’t. This means that you’re going to leave your opponent guessing and you’re going to get paid off a lot more when you have a hand.
The second reason continuation betting is profitable is that it allows you to win pots when you don’t have a hand and your opponent doesn’t either. Let’s look at an oversimplified example of poker before continuation betting as a bluff and poker after. Let’s say that in the old days, you have AK. You raise pre-flop, and your opponent calls with 10-9 suited. The flop comes out 8-4-2. Since it’s the old days and you have nothing, you decide to check. Your opponent, who also plays the old school game, decides to check as well.
The turn comes out and is a 10. You check again and your opponent bets because they have top pair. You only have ace high, so you elect to fold, and your opponent wins the hand.
Now, let’s take a look at this hand as it would play out if you were mixing in continuation betting as a bluff. You raise pre-flop with AK, and your opponent calls with the 10-9 suited. The flop comes out 8-4-2. You decide to continuation bet as a bluff, and your opponent, who has nothing, folds their hand. You win the pot. Yes, you did have the best hand, but you were able to take the pot down.
This also works when you don’t have the best hand. Let’s say you raise pre-flop with the AK again, and your opponent defends with pocket 3s. The flop comes out Q-9-6. Your opponent has the best hand with a pair of 3s. But you elect to continuation bet, and your opponent assumes that there is no way their pocket 3s are good on that board and they make the fold. You now win the pot with the worst hand because you elected to make a continuation bet.
Continuation bets will often win you the pot when both players have nothing and miss the flop. I say often because some people like to try and get tricky, which I cover in other advanced strategy sections. In the early days of continuation betting, people would fold no matter what if they didn’t have anything. You could continuation bet with 100% frequency, and it would turn a profit because it’s tough to hit flops.
People wised up to this and came up with strategies to combat 100% betting frequency. In response, people came up with MORE strategies to decide when they should continuation bet for maximum profitability. In the sections that follow, I’m going to walk you through how you should be deciding when you should continuation bet and also how you should be responding as a player against someone who is continuation betting.
Range vs. Range
The most basic way to start looking at when to continuation bet involves a little bit of theory into why these bets work. For now, I’m going to discount situations where you have a hand. When you have a hand, you should be betting most of the time. You already know this. What I want to talk about are the times that you miss the flop or think you miss the flop and need to decide what to do.
For continuation bets to be profitable when you miss the flop, your opponent needs to fold a fair amount of the time. For your opponent to fold, what needs to be going on? Well, your opponent is going to fold when they miss the flop. So, you should be looking to bet flops that miss your opponent’s range more often and hit your range more often.
If that last sentence confused you, that’s okay. I’m going to work through it step by step. First, so we are on the same page, a range is the potential hands that a player could have. When you’re trying to figure out what your opponent has, you never try and put them on one exact hand. You put them on a range of potential hands that they might have based on the information available in the hand. Your opponents will be doing the same to you. They’ll be trying to figure out what you have and will be assigning you a range based on the information that you’ve given away in the hand.
So, what you’ll want to do after the flop is put your opponent on a potential range of hands. This will be based on how they normally play, what hands they like to call with, what hands they do or do not 3-bet with, what position they are at on the table, any live tells, their stack size, and anything else you can analyze to get a better idea of what they might be holding.
You also need to be taking inventory of what range you’re supposed to have. Remember, this does not have to do with what you are actually holding, but what the rest of the table probably thinks you are holding. For example, if you have a shorter stack in a tournament, are a tighter player, and raise from under the gun, you could have 7-2, but the rest of the table is going to assume that you have a monster hand. This means that you can proceed as if you have the range that you’re supposed to have.
So, let’s look at the example I just gave, but extend it out a bit. Let’s say that you raise from under the gun, you have a shorter stack, and have been playing tight. You’re holding pocket 10s. It folds around to the big blind, who elects to defend. You know that the big blind is a player who loves to defend and rarely folds to a raise in the big blind. You also know that the big blind player 3-bets 100% of the time when they have a big hand, regardless of where the raise came from.
The flop comes out A-K-4. Is this a great flop for pocket 10s? No, it’s a pretty terrible flop. But this is a great flop for your potential range. While you hate the fact that there are two overcards on the flop, you’re supposed to have hands that smash that flop. Your opponent, on the other hand, is supposed to have hands that don’t hit that flop. If they had big aces or big pocket pairs, they probably would have re-raised pre-flop based on your history with them. They also call and defend with a wide range of hands, so it’s much less likely that they hit this flop.
What does this mean? This means this is a perfect spot for a continuation bet. What’s funny is that, based on the information provided, you likely have the best hand. A continuation bet, though, could get your opponent to fold out a weak king or something that could improve to beat you on the turn. The point is, though, this is a perfect spot because the board hits your range much more than it hits your opponent’s range. These are the spots you’re going to be wanting to continuation bet.
Will it work every time? No chance. But it only has to work a small percentage of the time to turn a profit. You’ll also have situations where you can barrel the turn and get your opponent off of a better hand based on your perceived range. For example, let’s say in the above example that the flop came out K-Q-4. You bet because the flop hits your range much more, but your opponent calls. The turn comes out an ace. This is a spot where you can bet again and continue your aggression because this card hits your range so much more than your opponent’s.
Your opponent will have to fold most of their floats (which we cover in another section) and queen pair hands, and they’ll be faced with a tough decision if they’re holding a king. Based on your tighter image in this example, a decent-sized bet will most likely get your opponent off of most of their king pair hands.
The more you understand ranges and the more you can dial down your opponent’s potential range, the more successful you’re going to be in picking the right times to continuation bet. If you’re always betting when they have a hand, you’re not going to see much profitability from your bets.
Board Textures
As I’ve already stated, continuation bets will win you the pot much more when your opponent does not have a hand. Yes, there are going to be instances where your opponents want to go to war, but that’s another discussion. In addition to looking at potential ranges, you can look at the texture of flops to help you decide whether a continuation bet should be warranted.
Is this any different from ranges? No, it’s actually just a part of it. But it’s a separate way you can look at flops to help you in situations where you’re struggling to make a choice on how to act.
Flops can be broken down into two main categories – wet and dry. The other terms you might use here are coordinated and uncoordinated. Let’s take a look at each separately and how this plays into ranges and continuation betting.
A dry flop is one that is uncoordinated, and you’re either going to hit the flop or miss it completely. For example, 8-2-2. You’re either going to have an 8, a 2, or absolutely nothing. There are no draws or any way you could kind of hit the flop. You either hit the flop or not.
A wet flop is one that is very coordinated where you can smash the flop, or you can somewhat hit the flop with draws. For example, let’s look at a flop like 9-10-J with two hearts. SOOOOOOO many hands hit this flop. If you’re holding even one 8 or one queen in your hand, you have a straight draw. If you have two hearts, you have a flush draw. Even if you only have the ace of hearts, you have a backdoor flush draw. So many more hands are going to hit this flop than are going to miss it.
Knowing this, which type of flop should you be more prone to bet? If you answered dry flops, you’re correct. The reason is because your opponent is going to miss this flop much more often than they hit it. This means that unless your opponent is stubborn, this is going to be a profitable play.
Who Starts Betting In Texas Hold'em
The problem with continuation betting on wet flops that you miss is that it’s much more likely that your opponent has a hand that they’re going to want to continue with. They might not have a super strong hand, but they’re often going to have a hand they’re willing to call at least one bet with. If the purpose of continuation betting as a bluff is to get your opponent to fold, it should make perfect sense why betting these type of flops is not going to be very profitable.
Frequency
I’ve already stated that when continuation betting started to grow in popularity, people were doing it with sometimes between 90% and 100% frequency. As you’ve seen in the strategy sections above, this no longer is something that can be done profitably. People are too willing to call down with more marginal hands, and people have a strange love and fascination with backdoor draws. While they do play a role in Texas hold’em, they’re much more important in games like PLO. You can probably blame PLO for the backdoor love trickling over into Texas hold’em.
So, this begs the question, should you bet every time that it’s a favorable range situation for you, or should you have some form of moderation? The answer is going to depend on a lot of factors. The best general answer I can give is that you should do it as often as you can profitably get away with it. The more pots that you can steal with nothing, the better, and the more you are betting as bluffs, the more likely people are to adjust and end up accidentally paying you off when you have a hand.
Frequency is going to depend on how your opponents are choosing to react to your bets, as well. If they’re “sticky” players who don’t like to fold, you may want to dial back your continuation bets a little bit. Remember, the whole goal is to get them to fold when you don’t have it, so if they aren’t folding, you may need to adjust. One way you can adjust is to dial back how often you are continuation betting. They’ll be less likely to fight you when you do bet, because they’ll give those fewer bets more respect.
On the flip side, if your opponents are playing too tight, you may want to up your frequency of continuation bets. Sometimes you’ll play with opponents who love to find reasons to fold and only like to continue after the flop with top pair, the nut draw, or better.
If you’re playing online and using a program like Hold’em Manager, you may want to spend some time reviewing the continuation betting results section. It will show you which flop types your bets are most successful on and which ones you’re failing on. With a large enough sample size, you can draw some pretty strong conclusions about the stakes and bank of players you are playing with. Small adjustments here can go a long way to strengthening your bottom line.
You want to try to be as balanced as you possibly can. What does this mean? This means that you can’t be doing the same thing every single time. If every time you check you don’t have a hand, people are going to auto-bet 100% of the time and steal all of these pots away from you. What I recommend doing is mixing in a few times that you don’t continuation bet with the best hand. Then, you can call down or check-raise the flop. Doing this a few times will keep your play balanced and stop your opponents from trying to rob you blind.
Firing Again
In the prior section, I left out something that is important because I wanted to cover it in full here. I first said that if people are calling your continuation bets too often, your response should be to continuation bet less. While this is one way you can adjust, there are other ways. One of the other ways you can combat this is by following up your continuation bet with a turn bet, and in some cases, another bet on the river.
Now, I want to start off with some words of caution. When you start barreling multiple streets, the pots get more expensive when you make mistakes. This means you need to exercise a little more caution and you need to be right as often as possible. While I’m not going to go fully into turn play today, I do want to leave you with a few thoughts to get your mind working in the right direction.
If you’re playing against an opponent who loves to call flop bets with very marginal hands like bottom pair or ace high, you may want to look into upping your turn bet frequency. While they may have the guts to withstand the first bet, it’s going to be really hard for them to stand up to a second and much larger bet on the turn. This will eventually get them to adjust and stop calling you on the flop as marginally.
You need to be ready to readjust if they do that. If they stop calling you so widely, it means that when they do call you on the flop, they’re going to be more likely to have a strong hand that is inviting more bets.
You can also look to bet more turns on cards that hit your range much more. Earlier in this guide, I had an example of betting an ace turn as it hit your potential range much more. Again, you need to be careful not to do any of this 100% of the time, because your opponents will figure it out and will adjust to exploit you.
The name of the game with firing on the turn is what you can and can’t get away with. You’ll know this based on who your opponents are, how they react to continued aggression, and where both of your perceived ranges stand. Remember, it’s not always about the cards you hold in your hand. A lot of times it’s just about what the rest of the table and your opponents perceive you to have.
Sizing
The last thing that I need to talk about regarding continuation betting is sizing. There are A LOT of different schools of thought here, so if you feel differently about this, you might not be wrong. I’ll give you what I feel is best and my reasoning behind it.
Typically, I like to continuation bet bigger on more coordinated boards, and slightly less on boards that are dry. Regarding the dry boards, your opponents are either going to have a big hand, or they’re going to have nothing. It’s going to be tough for them to make a call of any size if they have nothing, which means you can get away with a smaller bet. The times they do have a hand, you will lose less.
Regarding wet boards, you’re going to be betting more when you have a real hand to protect your hand. If you bet less when you’re bluffing, you’d be pretty easy to exploit. Your opponents would raise you every time you bet small and fold every time you bet big. The idea here is that you have to be congruent with what you would do when you had a real hand.
That’s the best rule of thumb that I can give you. Bet how you would if you actually had a hand that connected with the board. Otherwise, you are going to open yourself up to being exploited pretty easily and pretty quickly.
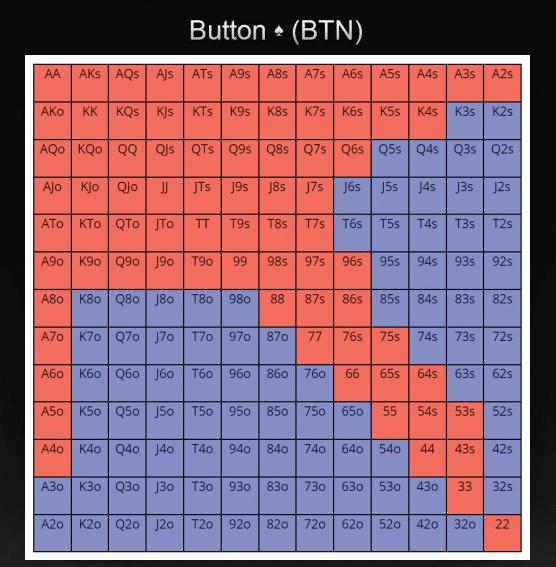
Texas Holdem Chart For Betting
Putting It All together
I sadly miss the days when blindly continuation betting was profitable, and people were easy to steamroll. Though those days are gone, continuation betting is still a profitable play, as long as you exercise a little bit of discretion and timing. It still helps to turn a big profit, as long as you don’t become predictable and allow yourself to be exploited.
With the tips I’ve given you, you should be ready to start employing this in your game or tweaking your current use of it. Remember, it all comes down to identifying ranges better. The better you are at reading what your opponent might have and reading what they are thinking you have, the better decisions you’re going to be able to make. This isn’t just true with continuation betting, but with all facets of your poker game.